Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act was established August 21, 1996. The four main purposes of HIPAA include- Privacy of health information, security of electronic records, administrative simplification, and insurance portability. The Act provides detailed instructions for handling and protecting a patient's personal health information.
The HIPAA Rules apply to covered entities and business associates.
A covered entity provides treatment, payment and operations in healthcare. Examples include: Doctor's office, dental offices, clinics, psychologists, Nursing home, pharmacy, hospital or home healthcare agency.
If a covered entity engages a business associate to help it carry out its health care activities, the covered entity must have a written business associate contract with the business associate that establishes specifically what the business associate has been engaged to do and requires the business associate to comply with HIPAA.
Hybrid Covered Entities
ASU has Hybrid Entities. These entities have business activities that include both covered and non-covered functions that designates units as health care entities.
For a Directory of ASU Hybrid Entities - Click here
HIPAA for Employees in a Covered Entity is designed for staff employed by ASU Health Services, ASU Counseling Services, ASU BioDesign COVID Testing Lab, Employee Health, Arizona Secure Research Environment, the University Technology Office, the Center for Health Information Research, and the Speech and Hearing Science Clinics. These are the eight units/departments that are included in the ASU Covered Entity under HIPAA regulations.
HIPAA Training
HIPAA for Employees in a Covered Entity:
The HIPAA for Researchers course was created specifically for The Center for Health Information Research as a supplementary course related to HIPAA regulations around research.
The HIPAA Lite course was created for individuals whose job responsibilities expose them to some protected health information but are not working within the Covered Entity. It is my understanding that EDGE does not restrict who can take any of the course, but the requirement for course completion depends on the department you work for.
HIPAA Students:
Anyone who handles HIPAA data is required to take training annually.
What is PHI?
Individually identifiable health information, including demographic information, that is created or received by a covered entity and that relates to the past, present, or future physical or mental health of an individual, provision of healthcare to an individual, or past, present, or future payment for the provision of healthcare to an individual. The presence of at least one of 18 HIPAA-designated direct and indirect identifiers in a data set makes the whole data set Protected Health Information.
- Name
- Social Security numbers
- Telephone numbers
- Addresses and all geographic information smaller than a state
- All elements of dates (except year), including date of: birth, admission, discharge, and death; and all ages over 89
- Fax numbers
- E-mail addresses
- Medical record numbers
- Health Plan Beneficiary numbers
- Account numbers
- Certificate/license numbers
- Vehicle identifiers and serial numbers, including license plate numbers
- Device identifiers and serial numbers
- Web Universal Resource Locators (URLs)
- Internet Protocol (IP) addresses
- Biometric identifiers, including finger and voice prints
- Full face photographic images and comparable images
- Any other unique identifying number, characteristic, or code: Any code or other means of record identification that is derived from PHI that must be removed in order for the data to be considered de-identified per the Safe Harbor method.
Tools
The Data Handling matrix provides a list of solutions that have already been evaluated for storing all classifications of data used at ASU, including sensitive and highly sensitive data. To use the data handling matrix, follow the guidance below:
- Identify the sensitivity and the regulated data type shown in rows 2 and 3 of the matrix.
- Then look for tools in the column that have been approved for that data type.
- Use this table to determine the next steps required for your chosen tool.
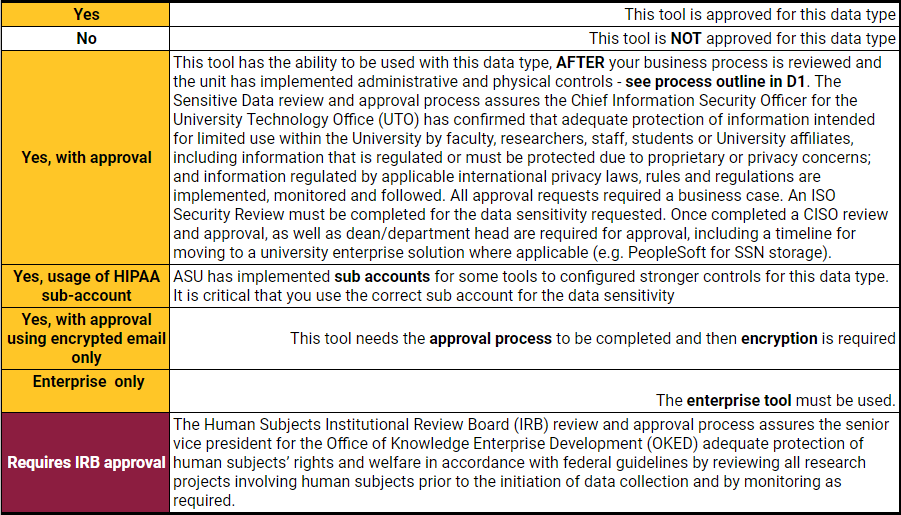
- If approval is required follow the process outlines in the diagram shown below.

References
- HIPAA Regulations for Research on Human Subjects
- HIPAA Basics for Providers: Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules
- Secure Emailing
- What is a HIPAA Covered Entity?
- What is PHI under HIPAA Rules? When is PHI not PHI?